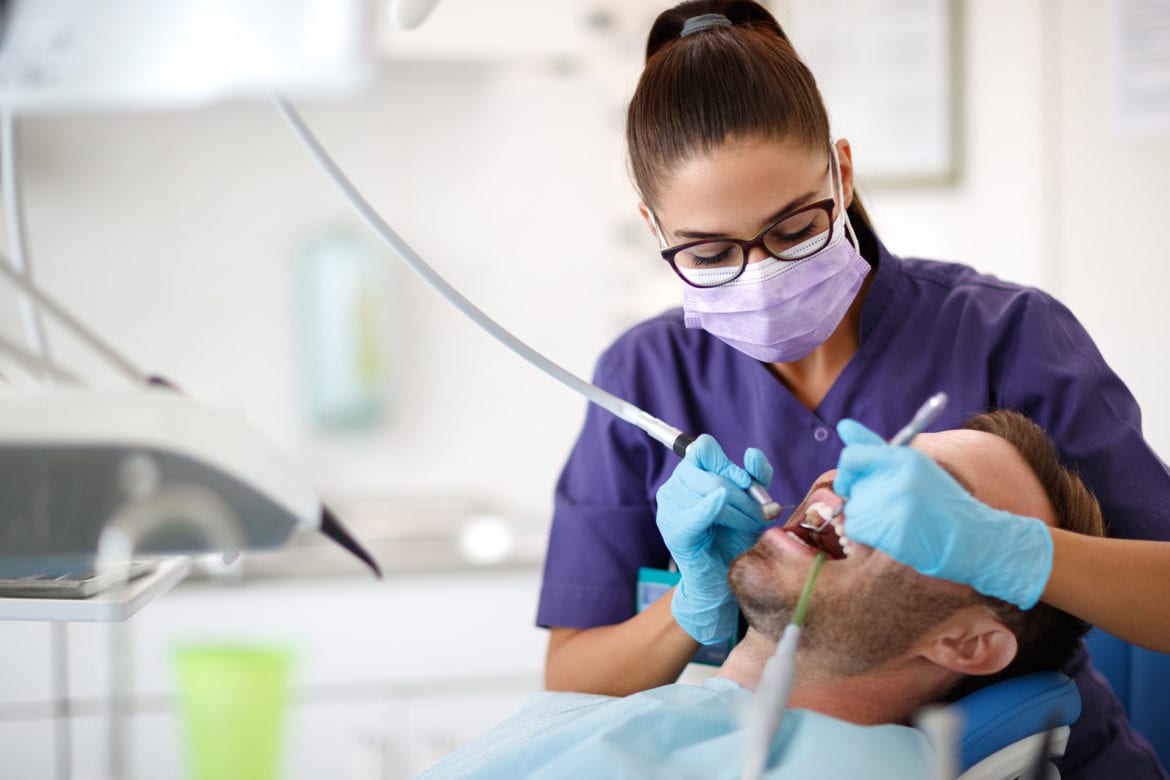
Dental procedures can pose a high risk of viral transmission because the tools that are used often produce aerosols, which can contain high numbers SARS-CoV-2 virions, copies of the virus causing COVID-19.
The aerosols are generated when saliva mixes with water and air streams used in dental procedures. As a result, access to routine dentistry continues to be limited during the current COVID-19 pandemic.
Dental practices, which are now back in operation, have had to introduce new room decontamination processes and personal protective equipment measures which have dramatically reduced the number of patients that can be treated in a single day. In particular, dentists need to leave long intervals between treatments, leaving rooms unoccupied to allow aerosols to dissipate. This is limiting patient access and challenging financial feasibility for many dental practices worldwide.
Now, researchers at Imperial College London and King’s College London have measured and analysed aerosol generation during dental procedures and suggested changes to prevent contamination in the first place to improve safety for both patients and the dental practice workforce.
They suggest that dentists avoid using dental drills that use a mixture of air and water as the abrasion coolants, and carefully select and control drill rotation speeds for those instruments that only use water as a coolant. Parameters have been identified that would allow some procedures such as dental fillings to be provided whilst producing 60 times fewer aerosol droplets than conventional instrumentation.
Lead author Dr Antonis Sergis of Imperial’s Department of Mechanical Engineering said: “Aerosols are a known transmission route for the virus behind COVID-19, so, with our colleagues at King’s, we have tested suggested solutions that reduce the amount of aerosols produced in the first place. These could help reduce the risk of transmission during dental procedures.”
Co-author Professor Owen Addison of King’s College London’s Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences said: “This important work describes the basic mechanisms that lead to the features of dental aerosols that we currently consider to be high risk. This has enabled us to choose drill parameters to keep our patients and the dental team safe at this difficult time. Although we cannot provide every procedure, because slowing our drills is much less efficient, we now have the basis to do more than we have done in the last 6 months.”
The results are published today in Journal of Dental Research and are already being included as evidence in guides for dental practices in the UK during the pandemic. The collaborative research used the engineering expertise at Imperial and clinical expertise at King’s College London’s Faculty of Dentistry, Oral & Craniofacial Sciences.
The researchers used dental clinical rooms at Guy’s Hospital in London to test how aerosols are generated during procedures such as decay removal, applying and polishing fillings and adjusting prostheses. They measured the aerosol generation using high speed cameras and lasers. They then used these findings to suggest modifications.
They found that using